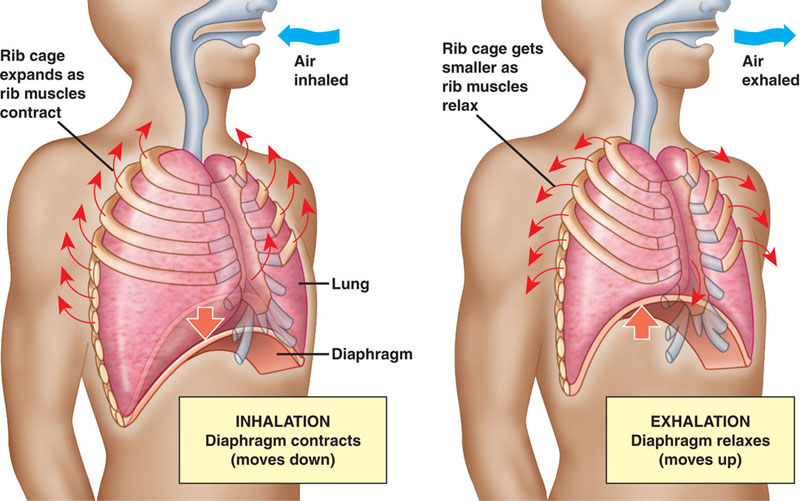
When the diaphragm muscle contract it pulls downwards creating more space on the surrounding of the lungs together with the rib cage expanding. The diaphragm flattens making the chest cavity smaller and air is sucked in.
The Amazing Diaphragm Foundational Concepts
Between the bony portions of the rib cage are two layers of intercostal muscles.

. During inspiration it contracts and flattens increasing the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity. When it is at rest it is slightly tense. Due to the gradient the air is from the atmosphere is.
What is position of diaphragm during inspiration. This is an important muscle that separates the thoracic cavity which contains the heart lungs and ribs from the abdominal cavity. The diaphragm helps in the inspiration and expiration of air in and out of the lungs.
Diaphragm is the muscle at the base of the lungs which aids during exhalation and inhalation. This produces lung expansion and air is drawn in. Between the costal cartilages however there is only one muscle layer and its fibers are oriented in a manner similar to those of the internal inter-costalsThese muscles are therefore called the.
What is position of diaphragm during inspiration. The diaphragm by contracting and relaxing changes the size of the thorax. In strenuous breathing the diaphragm may descend 10-12 cm 4 in which produces a pressure difference of 100 mmHg and the inhalation of 23 liters of air.
What functions does the diaphragm serve. It contracts and moves during inhalation. The diaphragm flattens making the chest cavity larger and air flows in.
5 Clinical Relevance. The diaphragm is a naturally curved muscle that sits between the thoracic and abdominal cavities. This will allow the lungs to.
Hence the person is able to inspire. Which describes the role of the diaphragm during inhalation. Maintain intra-abdominal pressure and act during expiration to push the diaphragm back up into the chest.
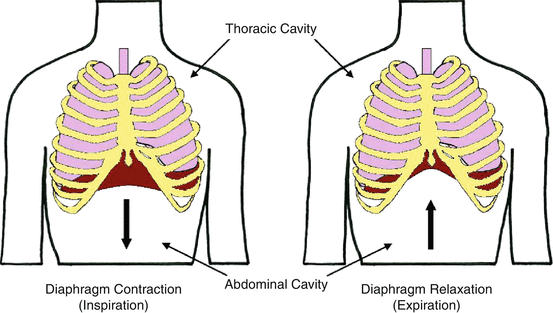
The pressure within the lungs is lesser than the atmospheric pressure the diaphragm contracts. Separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. During inspiration the diaphragm.
The diaphragm is a sheet of internal muscle which extends across the bottom of the rib cage. Sputum from a productive cough should be expectorated. Apply counterpressure to the flattening diaphragm to facilitate lateral and anteroposterior expansion of the chest.
It is attached anteriorly to the xiphoid process and costal margin laterally to the 11th and 12th ribs and posteriorly to the lumbar vertebraeThe posterior attachment to the vertebrae is by tendinous bands called cruraThe. Pressure gradients are generated with the help of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. The main role of the diaphragm in the human body is to assist with breathing.
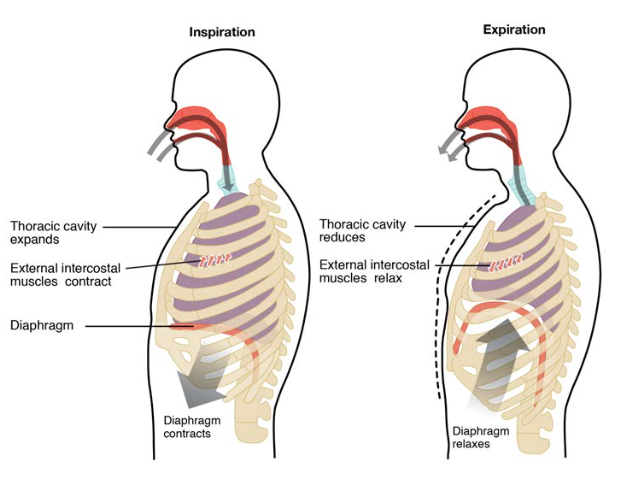
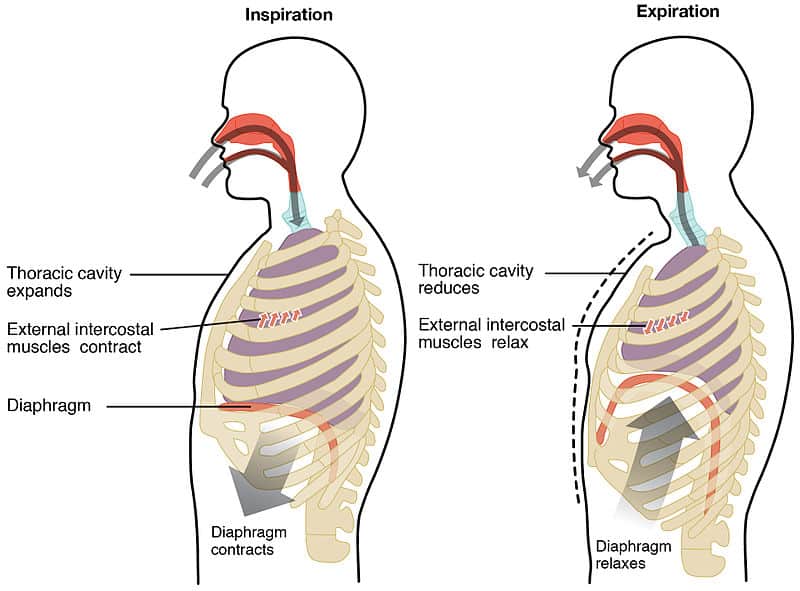
Inspiration occurs via active contraction of muscles such as the diaphragm whereas expiration tends to be passive unless it is forced. Undergoes contraction and relaxation altering the volume of the thoracic cavity and the lungs producing inspiration and expiration. When the intra-pulmonary pressure ie.
At the time of expiration the diaphragm relaxes reducing the. During expiration the diaphragm passively relaxes and returns to its original dome shape. The diaphragm is a musculotendinous structure with a peripheral attachment to a number of bony structures.
This increase in volume leads to a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure which is a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure and creates the pressure gradient. During normal quiet inhalation the diaphragm descends about 1-15 cm 04 in producing a pressure difference of 13 mmHg and the inhalation of about 500 mL of air. At the time of inspiration the diaphragm contracts increasing the pulmonary volume thereby reducing the intrapulmonary pressure to less than the atmospheric pressure and air moves into the lungs.
Inspiration is initiated by the relaxation of the. The diaphragm contracts during inspiration and relaxes during expiration. An element in hemothorax can tell you that the pleural cavity contains.
During a period of relaxed and average respiration the muscles associated with inspiration or the process of inhaling include the muscles of the diaphragm the external intercostal muscles and the interchondral region of the internal intercostal muscles. It contracts and relaxes during respiration to change the volume of the chest cavity. The diaphragm is the primary muscle of respiration.
Which statement best describes the diaphragms role in respiration. Active role whenever the respiratory effort is increased. During inspiration as a result of contraction of muscles attached to it the diaphragm.
Correct option is C During inspiration the diaphragm contracts and flattens to increase the volume of the the thoracic cavity. This reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. Inspiration occurs only when there is negative pressure in the lungs with respect to the atmosphere.
Expiration takes place only when intrapulmonary pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure. The external intercostal muscles and the internal intercostal muscles fig. This process lowers the air pressure in the lungs causing lower air pressure.
What is the role of the diaphragm. The contraction of the diaphragm increases the volume of the thoracic chamber thus increasing space for more air which is withdrawn during inspiration. The processes of inspiration breathing in and expiration breathing out are vital for providing oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide from the body.
The diaphragm acts as the ____ of the thoracic cavity and the ____ of the abdominal cavity. During inhalation the diaphragm begins to move downwards and flattens which allows the lungs to expand and accommodate air. Origin and insertion.
During inspiration the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the main muscle for both inspiration and expiration in most animals birds dont have a diaphragm. When we say diaphragm we generally refer to the thoracic diaphragm that helps in breathing.
The diaphragm moves upward making the chest cavity smaller and air is pushed out. Inhalation is the process of breathing inWhen you breath in the diaphragm contracts and moves downwards This makes the spaces in the chest to expand and lungs increases in sizeThe air then enters the lungs to minimise the pressure in the lungsThe external intercostal muscles contract making the ribs to move outwards and inwards and they.
The Process Of Breathing Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Mechanics Of Breathing Inspiration Expiration Teachmephysiology

0 Comments